The key points of the final report are:
- EU-15: Emissions of GHGs decreased by 0.8% (35.2 million tonnes CO2 equivalents) between 2004 and 2005 - mainly due to decreasing CO2 emissions
of 0.7 % (26 million tonnes).
- EU-15: Emissions of GHGs decreased by 2.0% in 2005 compared to the base year[1] under the Kyoto Protocol.
- EU-15: Emissions of GHGs decreased by 1.5% between 1990 and 2005
- EU-27: Emissions of GHGs decreased by 0.7% (37.9 million tonnes CO2 equivalents) between 2004 and 2005
- EU-27: Emissions of GHGs decreased by 7.9% compared to 1990 levels
[1] The base year for most greenhouse gases under the Kyoto Protocol is 1990 for the EU-15, but almost all Member States use 1995 as the base year for fluorinated or
'F-gases'
Which EU-15 countries show the biggest decreases in GHG emissions?
Germany, Finland and the Netherlands contributed most to the EU-15 reduction in absolute terms (see table in Notes to the Editor). Reduction of CO2 emissions drove the
overall decrease of greenhouse gas emissions in these countries.
- Germany reduced emissions by 2.3% or 23.5 million tonnes CO2 equivalents: a shift from coal to gas in the production of public electricity and heat was one
of the main reasons for the decrease in emissions. In addition, emissions from road transportation and from households and services declined substantially.
- Finland reduced emissions by 14.6% or 11.9 million tonnes CO2 equivalents: emission reductions were mainly due to a substantial decrease in the use of
fossil fuels in the production of public electricity and heat mainly due to electricity imports. Coal use, in particular, decreased.
- The Netherlands reduced emissions by 2.9% or 6.3 million tonnes CO2 equivalents: less fossil fuel was used for the production of public electricity and
heat. The household and service sector used less fuel due to a warmer winter
Other EU-15 countries which saw emissions decrease between 2004 and 2005 are: Belgium, Denmark, France, Luxembourg, Sweden and UK.
Which sectors are mainly responsible for the GHG cuts?
In absolute terms, the main sectors contributing to emissions reductions between 2004 and 2005 in the EU-15 were public electricity and heat production, households and
services, and road transport.
CO2 emissions from public electricity and heat production decreased by 0.9% (-9.6 million tonnes) mainly due to a reduction in the reliance on coal.
CO2 emissions from households and services decreased by 1.7 % (7.0 million tonnes). Important decreases in emissions from household and services were reported
by Germany, the United Kingdom and the Netherlands. One general reason for the decrease is the warmer weather conditions (milder winter) compared to the previous
year.
CO2 emissions from road transport decreased by 0.8% (6 million tonnes). This is mainly attributed to Germany, and is due to increased amounts of diesel oil
driven cars, the effects of the eco-tax and fuel buying from outside Germany (fuel tourism).
Which EU-15 countries have seen the biggest increases in GHG emissions?
In absolute terms, Spain increased greenhouse gas emissions the most between 2004 and 2005 (see table in Notes to the Editor).
In Spain, the increase in greenhouse gas emissions by 3.6% or 15.4 million tonnes CO2 equivalents came mainly from public electricity and heat production. This
is due to a rise in electricity generation from fossil thermal power stations (17 %) and a decrease in electricity generation from hydropower plants (-33 %).
Other EU-15 countries which saw emissions increase between 2004 and 2005 are: Austria, Greece, Ireland, Italy and Portugal.
The EEA GHG data viewer
The EEA GHG data viewer is an interactive tool that allows easy web access to the main data contained in the EC Greenhouse gas inventory report. The GHG data viewer
enables the user to view and analyse emission trends for the main sectors and their sub sectors. It also facilitates comparison between emissions from selected countries
and sectors. In addition, the GHG data viewer enables the production of graphics and the downloading of key emission estimates.
EEA GHG Data Viewer
Notes to the Editor:
What is the annual GHG inventory report?
This report is the EU's official submission to the UNFCCC on total domestic greenhouse gas emissions for the period 1990-2005. Domestic, in this context, refers to
emissions from within the territory of the EU. It contains information about GHG emissions for the EU-15 and EU-27. It also thoroughly explains the process by which EU
emissions are derived and quality checked.
The EEA is responsible for compiling and publishing this report annually using information reported by national governments under the EC GHG Monitoring Mechanism.
How does the information in the report fit with the EU Emission Trading Scheme?
In 2005 the EU Emission Trading Scheme (EU ETS) covered approx. 47% of the total CO2 emissions and approx. 39% of total greenhouse gas emissions in EU-15.
The EU ETS covered approx. 49% of the total CO2 emission and 41% of total greenhouse gas emissions in EU-25. In general, EU ETS information has been used by EU
Member States as one input for calculating total CO2 emissions for the Energy and Industrial Processes sectors in this report. However, an explicit
quantification of the contribution of the EU ETS to total CO2 emissions at sectoral and sub-sectoral level is not yet available for EU-15 or EU-25.
What is the significance of this report in the context of the Kyoto Protocol?
The EU-15 has a common target under the Kyoto Protocol to reduce total greenhouse gas emissions by 8 %, compared to the base year. The EU-27 does not have a common
Kyoto target. Official reporting of emissions for compliance purposes under the Kyoto Protocol does not begin until 2010 – when emissions will be reported for the year
2008. In the meantime, this report is the most relevant and accurate source of information on greenhouse gas emissions for the EU. It can be used for tracking the EU's
performance when it comes to reducing domestic greenhouse emissions (i.e. emissions within its territory) towards meeting the Kyoto targets. Parties to the Kyoto Protocol
are allowed to use carbon sinks as well as the so called 'flexible mechanisms' to further reduce greenhouse gas emissions outside their national territories - as a
supplement to domestic reductions. Hence, domestic action is the primary method of achieving the Kyoto targets. This inventory report suggests that domestic emissions of
GHGs decreased by approximately 2.0 % compared to the base year under the Kyoto Protocol.
Table 1: Greenhouse gas emissions in CO2 equivalents (excluding carbon sinks) and Kyoto Protocol targets for 2008–12
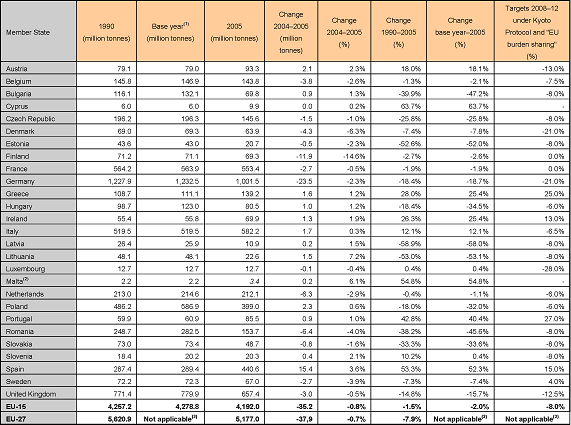
(1) For EU-15 the base year for CO2, CH4 and N2O is 1990; for the fluorinated gases 12 Member States have selected 1995 as the base year, whereas Austria, France and
Italy have chosen 1990. As the EU-15 inventory is the sum of Member States' inventories, the EU-15 base year estimates for fluorinated gas emissions are the sum of
1995
emissions for 12 Member States and 1990 emissions for Austria, France and Italy. The EU-15 base year emissions also include emissions from deforestation for the
Netherlands, Portugal and the UK (‘The European Community's initial report under the Kyoto Protocol' (EEA, 2006)).
(2) Malta did not provide GHG emission estimates for 2005, therefore the data provided in this table is based on gap filling (see Chapter 1.8.2.).
(3) EU-27 does not have a common Kyoto Protocol target
Note: Malta and Cyprus do not have individual Kyoto targets.
What is the EU-27?
EU-27: Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxemburg,
Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, United Kingdom.
What is the EU-15?
EU-15: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden, United Kingdom
Links:
To view the full report, see: Annual European Community GHG inventoy 1990-2005 and inventory report
2007
For FAQs about the GHG inventory report, see: FAQ
For access to GHG data, see: EEA GHG data viewer


Document Actions
Share with others