3. Large point source
Emissions in Europe 1990
3.1. Introduction
More data is generally needed for
modelling and for compliance monitoring of large point sources in comparison to area
sources. CORINAIR 90 provides the information on large point sources (LPS).
The emissions of these sources are
especially interesting, firstly because they are responsible for poor local ambient air
quality and, secondly because emissions from LPS contribute to long range transport of air
pollutants.
3.2. Overview
For some pollutants large point
sources (LPS) are responsible for a considerable share of the total European emissions
(see table 9).
Table 9: Overview of European Emissions in
CORINAIR 90
Pollutant |
Emissions in ktonnes |
|
Area sources |
% |
LPS |
% |
Total |
| SO2 |
9
034 |
32 |
18
839 |
68 |
27
874 |
| CO2 |
3
036 399 |
64 |
1
728 064 |
36 |
4
764 463 |
| NOx |
13
130 |
73 |
4
792 |
27 |
17
923 |
| N2O |
1
608 |
86 |
271 |
14 |
1
880 |
| CO |
64
493 |
93 |
5
219 |
7 |
69
712 |
| NMVOC |
21
120 |
97 |
650 |
3 |
21
770 |
| CH4 |
44
708 |
98 |
707 |
2 |
45
415 |
| NH3 |
5
649 |
99 |
52 |
1 |
5
701 |
Details on total emissions for all eight pollutants have already been published in the
CORINAIR 90: Summary Report nr. 1 and nr. 2.
Figure 4 shows that SO2,
NOx and CO2 emissions of LPS are responsible for more than 20% of
the European total. SO2 is particularly interesting, where 68% of the total
emission is caused by large point sources.
This chapter presents data on LPS
for SO2, NOx, CO2.
Figure 4: Percentage of the LPS emissions in
CORINAIR 90
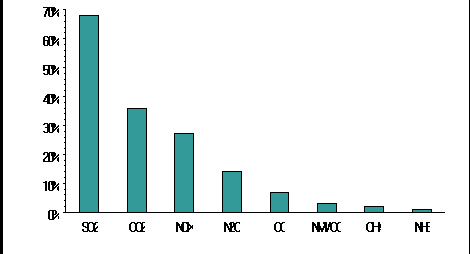
CORINAIR 90 distinguishes
between a number of different air emission sources. Emissions from LPS are highly
concentrated in a very few sources. This report therefore presents only LPS results for
four source sectors. (see table 10).
Table 10: LPS emissions in Europe per source
sector
| Source
sector |
Emissions in ktonnes |
|
SO2 |
% |
CO2 |
% |
NOX |
% |
| Public Power Plants
>300MW |
13
691 |
74 |
1
160 276 |
67 |
3
316 |
69 |
| Industrial
Combustion Plants >300MW |
1
781 |
9 |
178
877 |
10 |
430 |
9 |
| Refineries |
635 |
3 |
58
322 |
3 |
121 |
3 |
| Inorganic Chemical
Industries |
201 |
1 |
9
726 |
1 |
136 |
3 |
| Other |
2
531 |
13 |
320
862 |
19 |
772 |
16 |
| Total LPS emissions |
18
839 |
100 |
1
728 063 |
100 |
4
775 |
100 |
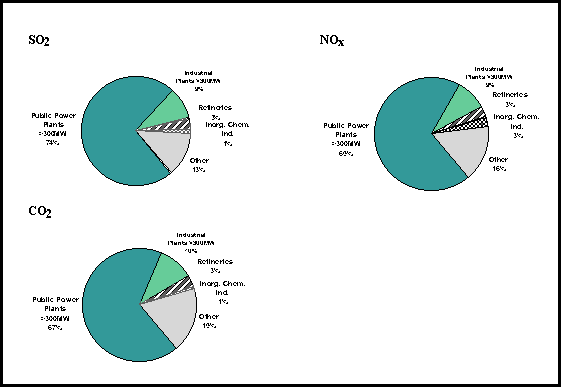
The relative contribution of these
four source sectors is given in figure 5, showing that Public Power Plants are by
far the biggest source of LPS emissions.
Figure 5: Relative contribution of source
sectors to LPS emissions
From the vast amount of
information on LPS made available in CORINAIR 90 the next chapter will present the ten
largest LPS for SO2, NOx and CO2 for the source sectors
mentioned above.


Document Actions
Share with others