1. Current CORINAIR 90 System
The current CORINAIR 90 system is a conspicuous milestone on the
road of Air Emission Inventories in Europe.
It results of developments in the frame of the CORINE programme. A
first generation was provided to compile the EC emission inventory for 1985 (CORINAIR 85)
and the current second generation used for CORINAIR 90 emission inventory now under
responsibility of the EEA (1).
1.1 The four dimensions
The CORINAIR system is based on the four dimensional aspects which
need to be specified according to objectives of each inventory.
CORINAIR 90 dealing mainly with acidification, photochemistry and
greenhouse effects, the selected substances have been SO2, NOx, NMVOC, CH4, CO, CO2, N2O
and NH3.
The split of some substances in different species (i.e. VOC's) had
been identified as a relevant need but not considered as a priority.
More than 240 emitting activities are defined in the Selected
Nomenclature for Air Pollution (SNAP). Emitters correspond to relevant combinations of
SNAP activity + fuel (for energy related activities) + supplementary
rubric (optional).
Fuels are defined in NAPFUE and rubrics are free for more split by
producers of inventories.
Main emitters are classified as Large Point Sources (LPS) according
to specifications to be adapted with inventory objective. Individual information is
collected for LPS.
Remaining emitters are classified as Area Sources (AS) for which
activity rates and emission factors are requested.
The general formula used is :
E = S [ Ai,f,r x Efi,f,r,p ]
where E is the total emission for a pollutant p
Ai,f,r is a representative value of the activity i
EFi,f,r,p is the emission factor assigned to activity i fuel f,
rubric r and pollutant p.
For LPS, emissions are determined either from direct emission
estimations (measurement, balance, or from calculation by the mean of emission factors.
CORINAIR 90 is based on administrative territorial units defined by
EUROSTAT (NUTS levels 0 to III or equivalent for non EU countries) because statistics are
generally more available at this scale than at any grid square. Moreover, this resolution
fits fairly well with modelers needs in Europe.
Nevertheless, a lot of air emission inventory requests deal mainly
with the national level only.
A special allocation procedure involving socio economical data (e.g.
population, area, employment, number of houses, ...) is provided to perform activity rate
estimation at territorial units levels for which the requested data are not available.
There is interest for high time resolution (e.g. modelization of
photochemistry) but such figures can be more easily produced from an annual basis which
fits with most of mains uses of air emission inventories.
1.2 Processing overview
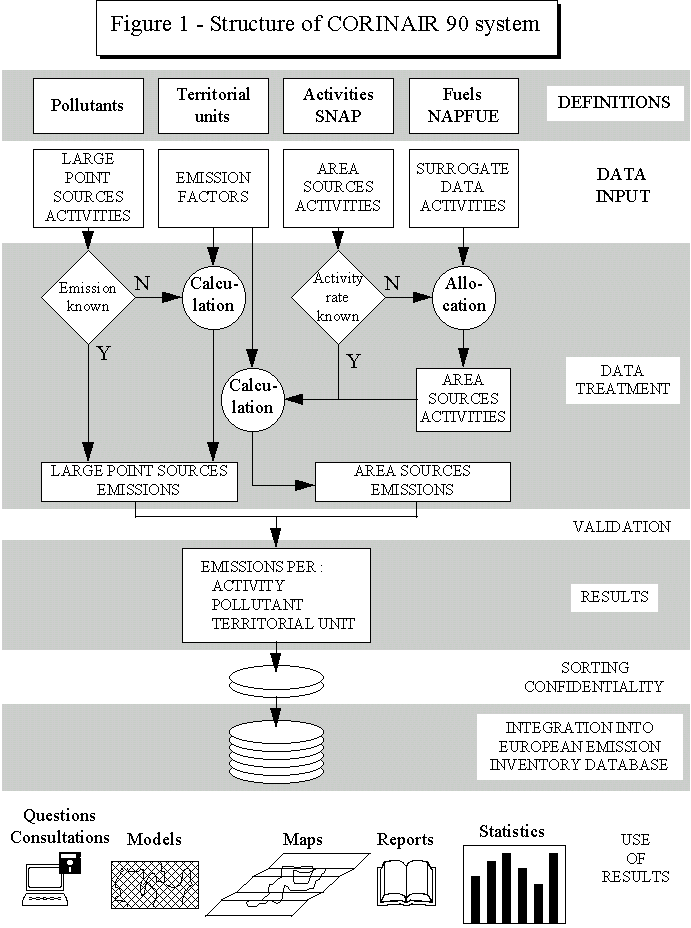
The CORINAIR 90 system is described in figure 1 and includes the
following steps :
- National/producer level definitions/specifications for source
categories, fuels, territorial units, pollutants, LPS, surrogate data, units, ...
- Collection of data (activity rates, emission factors, fuel
characteristics, LPS information, comments, surrogate data, ...)
- Data treatment (allocation procedure, emission calculation, checking)
- Each national database is examined by the CORINAIR Technical Unit for
checking on consistency and completeness. Analysis of emission factors discrepancies
enables to detect irrelevant figures and to help to increase their relevancy.
- All validated national databases are transfered to the EEA ORACLE
System and constitute the centralized CORINAIR database
- Outputs such as reports, maps, databases, ...are produced
It is to be noticed that bottom-up and top-down approaches are used
respectively for large point sources and area sources allocation.
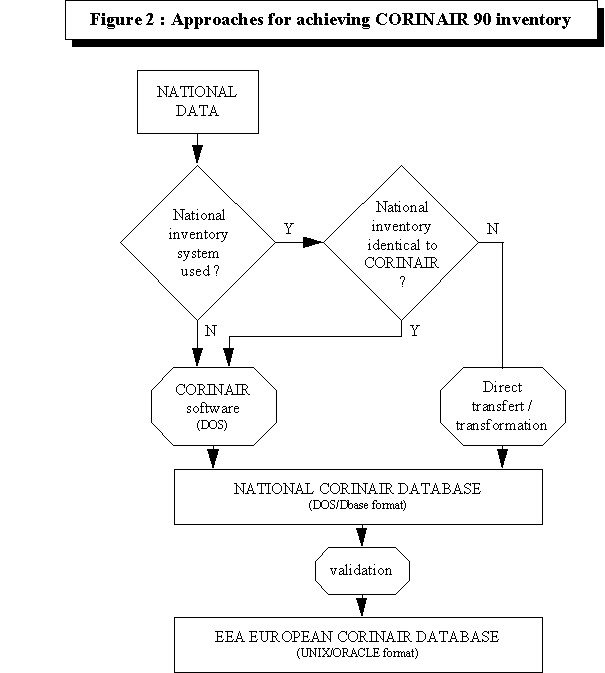
Practically, two approaches are used (cf figure 2) :
- One for countries who export data from their national specific system
to CORINAIR database (Dbase format). When the national system does not cover all data
requests, the CORINAIR software may be used for completion of the database.
- Other countries use the CORINAIR software to achieve their CORINAIR
emission inventories.
1.3 Tools of CORINAIR 90 system
Different tools have been developped to reach objectives of CORINAIR
90 inventory :
- set of common definitions and specifications (SNAP, NAPFUE,
pollutants, LPS),
- Handbook of Emission Factors in order to help producers of emission
inventories. This handbook is changed in a more structured Guidebook which will be
available in mid 1995 (EMEP/CORINAIR Guidebook),
- software allowing to store, to manage inventory data and to provide
emission estimations by each producer (2),
- validation routines for various checkings,
- routines for data transfer from DOS/Dbase platform to UNIX/ORACLE
platform, due to some differencies in data dictionaries (2) (3) and difference of
platforms,
- CORINAIR/IPCC interface,
- procedure for allocating emissions from administrative territorial
units to EMEP grid.
1.4 Data in CORINAIR 90 system
Data are classified according to the following understanding (4)
Essential. This is the most important information that must
be included in any inventory produced by the EEA.
Desirable. These data items should be included but their
priority is lower. These are items that will become available on a longer time frame. For
example, the full documentation of an inventory is required but can be published after the
results become available.
Useful. Some items of data would be useful to have but are
not necesary to the overall project. For example, all the details of a power plants
boilers are not needed at the European level and so this data would be useful but not
essential or desirable.
Definition/reference data
| Pollutant |
F |
essential |
| SNAP |
F |
essential |
| NAPFUE |
F |
essential |
| Fuel characteristics |
N |
useful (depending on producers) |
| Annex rubric |
N |
desirable |
| Elementary area activity |
N |
essential |
| PoActivity group |
F |
essential |
| Territorial unit |
F/N |
essential |
| Surrogate data |
N |
essential or not used (depending on approach) |
| Control device |
F |
useful |
| Estimation method |
F |
useful |
| Unit |
F |
essential |
| Mass unit conversion |
F |
essential (data system) |
| Comment source of information |
N |
desirable |
| Surrogate relations |
N |
essential or not used (depending on approach) |
F = forefilled
N = not forefilled
COLLECTED OR ESTIMATED DATA
General
| data quality indicators |
desirable |
| comments and sources of information |
desirable |
| confidentiality indicators |
essential |
Area sources
| activity unit |
essential |
| emission factor |
essential |
| activity rate |
essential |
| activity unit ratio between reference unit and used
unit |
essential |
| surrogate data rate |
essential when allocation procedure is used |
Large Point Sources (LPS)
| identification data (LPS code. T.U.,
coordinates...) |
essential |
| estimation method |
efficiency of control device useful
possibly desirable for some users |
| emission rate |
essential when emissions are directly known
(measurements, ...) |
| activity rate and unit |
essential when use of emission factors or
for some outputs (IPCC); desirable in other cases |
| emission factor |
essential when use of emission factors
otherwise not used |
| fuel consumption |
essential for some outputs (IPCC) and
calculation facilities ; otherwise desirable |
| basic fuel emission factor |
essential for some outputs (IPCC) and
calculation facilities ; otherwise desirable |
| fuel LHV |
essential for some outputs (IPCC) and
calculation facilities ; otherwise desirable |
| Stacks characteristics (height, flow rate,
...) |
useful possibly desirable for some users |
| other characteristics (nominal
capacity,starting year, working time) |
useful |
| LCP Directive data (plant statute
(existing/new), corrected thermal capacity |
essential for some outputs (LCPD) |
Output data
The system enables outputs of following kinds of data :
- reference definition data
- data collected
- data estimated by software process (activity rates estimated by the
use of surrogate data)
- emissions processed by the software which are obviously essential



Document Actions
Share with others