
This report looks at how biomass can help us reach our climate and environmental objectives, and how climate change might affect the EU's biomass production in agriculture and forest sectors. It also discusses key synergies and trade-offs in the use of biomass for different policy objectives.

This decade will see significant decarbonisation of the EU electricity supply. Brave
changes are happening, driven by the expected rapid roll-out of wind and solar power
generation in all Member States in response to the Russian war of aggression against
Ukraine and Europe's commitment to become a 'net-zero' emissions continent by
2050 (expressed in the 'Fit-for-55' and the forthcoming EU climate target for 2040).

The ways in which societies, institutions and citizens relate to and value nature have played a key role in the interconnected biodiversity, climate change, natural resource and health crises we face. This briefing explores how to reframe the relationships between humans and nature. It examines how holistically understanding humans’ deep interconnection with other life forms and ecosystems could lead to new motivations to protect nature and accelerate the societal transformation we need to live well within the limits of the planet.

The EU has met its target to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 20% by 2020, compared with 1990 levels. However, meeting targets for 2030 and beyond requires a doubling of the annual reduction in greenhouse gas emissions achieved between 2005 and 2020. Heating and cooling account for half of the final EU energy use. With energy used for heating being significant, decarbonising heating is therefore critical. Solutions to save energy and introduce efficient, renewable heating and cooling systems exist and must be rolled out faster. This briefing looks at heating and cooling trends across the EU. It highlights the twin benefits — for climate mitigation and security of supply — of combining energy efficiency and conservation measures with rapidly switching to renewable and waste energy use in heating and cooling.

In an increasingly urbanised world, cities and municipalities play a key role in the energy transition and the decarbonisation of society. Prosumers (producers-consumers) of renewable energy can help accelerate this transition in cities. This briefing builds on recent EEA work on prosumption by focusing on the challenges and opportunities that urban areas present, and on how local authorities can promote prosumption in their cities.
This dataset contains the location and administrative data for Large Combustion Plants in the Energy Community participating countries, as well as more detailed data on energy input and emissions to air. These data are reported to EEA under the Energy Community Treaty. Warning: Reporting countries have only recently started to report and it is expected that data quality will increase as experience in reporting consolidates. Countries will be correcting the reported data and updates will be posted accordingly. The metadata document provides further information on this matter. Data covers 2018-2021.

Renewable technologies create new opportunities for citizens to become energy producers themselves and to actively contribute to the energy transition. This report provides an overview of the role of renewable energy prosumers in Europe, including case studies on successful initiatives.

The year 2020 saw remarkable progress towards meeting the EU's climate and energy targets. Rarely in the publication of the annual Trends and projections in Europe report has this executive summary presented such substantial progress as this edition does. Preliminary estimates indicate that, in 2020, we witnessed the full achievement — and even overachievement — of Europe's 20-20-20 goals for climate change mitigation, renewable energy deployment and energy efficiency gains. This keeps Europe well on track in its journey towards climate neutrality by mid-century.

Renewable energy technologies, such as wind turbines, solar photovoltaic panels and batteries, are essential for Europe’s transition to climate neutrality. Deployment, maintenance and replacement of this infrastructure requires significant resources, including many substances included in the EU list of critical raw materials. Waste arising from end-of-life clean energy infrastructure is projected to grow up to 30-fold over the next 10 years, presenting significant opportunities to reduce consumption of scarce raw materials by recycling metals and other valuable resources back into production systems. Circular economy approaches such as repair and upgrading of equipment and recycling up to 90% of end-of-life infrastructure can underpin the sustainability credentials of Europe’s renewable energy transition.

We need to invest in a green recovery to restart the economy. The European Green Deal puts climate change mitigation at the core of its efforts to recover sustainably from the COVID-19 crisis. Renewable electricity could increase to 70% of all power generation by 2030 to allow a net 55% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. Despite multiple benefits for human health and the environment associated with the reduction in fossil fuel use for energy, increasing renewable power supply is not impact free. Concerns have been raised that renewable electricity could shift environmental burdens in ways that do not always lower overall pressures. This briefing investigates changes in the electricity mix since 2005, and their trade-offs from a life cycle perspective to help policymakers and individuals focus on areas that offer opportunities for improvement.

This briefing looks at the challenges posed by cross-border cooperation on renewable energy. It analyses the barriers holding countries back and makes recommendations to overcome the challenges, based on the experience of three case studies on cooperation between Denmark and Germany, Norway and Sweden, and Ireland and the United Kingdom.

Tracking progress towards Europe’s climate and energy targets. The annual ‘Trends and projections’ report provides an assessment of the progress of the EU and European countries towards their climate mitigation and energy targets. It is based on national data for greenhouse gas emissions, renewable energy and energy consumption.

This report analyses the developments of the official EU data submitted to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) from 1990 to 2018. It also provides a short summary of the results for 2018 compared with those for 2017.

The European energy system is undergoing rapid changes to set the EU economy on a low-carbon and resource-efficient path. Renewable energy is instrumental to this transformation. EU efforts to double the share of renewable energy in its consumption have paid off, having reduced significantly the amount of fossil fuels used and their associated greenhouse gas emissions. Concerning air pollutant emissions however, the outcomes were not always positive: in countries where biomass burning has increased considerably since 2005, emissions of certain air pollutants have also increased. This briefing presents an estimate of the impact of renewable energy consumption on fossil fuel use, greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) and air pollution since 2005.

The annual ‘Trends and projections’ report provides an assessment of the progress of the EU and European countries towards their climate mitigation and energy targets. It is based on national data for greenhouse gas emissions, renewable energy and energy consumption.
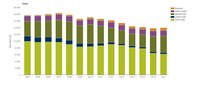
EEA indicator
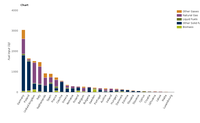
EEA indicator
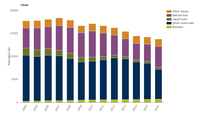
EEA indicator

Building a climate‑resilient low‑carbon energy system

This report introduces several methods the European Environment Agency (EEA) has developed for assessing and communicating early RES growth and the important knock-on effects that RES growth has on the energy sector and related areas. The report provides specific information at EU and country level on estimated RES progress in 2013, estimated gross avoided carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and avoided fossil fuel use due to the additional use of renewable energy since 2005, as well as an assessment of the statistical impacts of growing RES use on primary energy consumption.
Document Actions
Share with others