
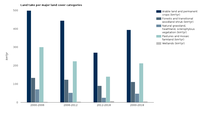
Trend of sites designated under the EU Habitats and Birds Directives
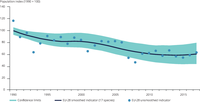
The indicator the population trends of European grassland butterflies
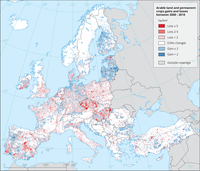
This map shows the loss and gain of arable land and permanent crops. Changes are monitored at 1 ha level whereas the map is aggregated in a 10 km2 grid.
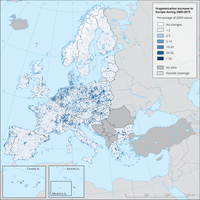
The map shows the difference of the years 2015 and 2009 and presents the increase in fragmentation in that period. The original 100m values were resampled to a 5 km grid for visualisation purposes.
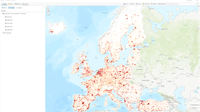
The map viewer of the Integrated Data Platform visualizes spatial datasets by web map services. Those spatial datasets are selected which are frequently used in assessments. The web map viewer enables spatial overlays so that the datasets can be interactively explored. Through exploring the datasets their potentials in environmental assessments can be better understood.

Biodiversity collectively describes millions of unique living organisms that inhabit Earth, and the interactions among them. They represent a vital element of our lives but are under continuous threat. The conservation status of more than 60% of species and habitats protected under the EU Habitats Directive is unfavourable. This has fundamental consequences for our society, economy and human health.

Facebook Live interview on Climate Change.

The JRC PESETA III project has developed projections of the Canadian Fire Weather Index (FWI) for various climate change scenarios.

The map shows an overview of protected sites in Europe. The EU’s Natura 2000 network and the Bern Convention’s Emerald Network are ecological networks of protected areas, set up to ensure the survival of Europe's most valuable species and habitats. Information about protected areas designated at national levels is reported by the 38 countries of Eionet.

This indicator describes the levels of and trends in the levels of eight hazardous substances in marine biota in European seas , based on individual assessments of monitoring data for the following substances:
mercury (Hg) and its compounds;
cadmium (Cd) and its compounds;
lead (Pb) and its compounds;
HCB;
PCBs, using chlorinated biphenyls CB28, CB52, CB101, CB118, CB138, CB153 and CB180 as representatives;
the pesticide DDT (using pp’DDE as a representative);
the pesticide Lindane (1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane);
the polyaromatic hydrocarbon BaP.
The indicator is based on data on the levels of these substances measured in organisms from the regional seas as follows:
Baltic Sea — Atlantic herring (Clupea harengus);
North-East Atlantic Ocean — blue mussel (Mytilus app), Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua), flounder (Platichtys flesus);
Mediterranean Sea — Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovinicialis);
Black Sea — Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovinicialis).

EUROPEAN COMMISSION, 2019 Public Opinion

Using big data from Copernicus Land Monitoring Service, as well as other satellite and user data sources, Viridian Raven has developed a set of algorithms that gives a risk analysis of bark beetles in forests. This enables foresters to see which parts of their forests have a high risk of bark beetle activity and enables fieldwork to be carried out more effectively saving time and allowing for more nests to be found earlier.

Soil plays a crucial role in nature’s cycles, including the nutrient cycle, which involves how much soil organic matter — i.e. carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus — is taken up and stored in soil. Organic compounds, such as leaves and root tips, are broken down to simpler compounds by organisms living in soil before they can be used by plants. Some soil bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into mineral nitrogen, which is essential for plant growth. Fertilisers introduce nitrogen and phosphates to induce plant growth but not all amounts are taken up by plants. The excess can enter rivers and lakes and affect life in these water ecosystems.
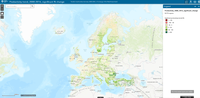
This data viewer provides information about the land cover and land cover change within and outside the Natura 2000 network.

EXIOBASE is a global, detailed Multi-Regional Environmentally Extended Supply-Use Table (MR-SUT) and Input-Output Table (MR-IOT). It was developed by harmonizing and detailing supply-use tables for a large number of countries, estimating emissions and resource extractions by industry. Subsequently the country supply-use tables were linked via trade creating an MR-SUT and producing a MR-IOTs from this. The MR-IOT that can be used for the analysis of the environmental impacts associated with the final consumption of product groups.
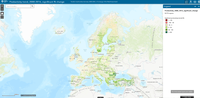
This interactive data viewer provides a set of dashboards giving an overview of the land take and net land take processes for Europe (EEA39 and EU28) derived from the CORINE land cover data series. Statistics are derived for every 6 years of the acquisition period, as well as for the entire period (2000-2018). The viewer facilitates the assessment of land take over a specific period as well as the land use drivers of the observed changes, which can be analyzed within user defined spatial units such as administrative regions, biogeographical regions or land cover classes.
This dataset refers to the Richness index of Species and Habitats of Conservation Concern indicator. This indicator has been developed to be used as a sub-indicator for contributing to the identification of the High Nature Value (HNV) Forest Areas as it will be integrated with other sub-indicators of horizontal structure, management and naturalness to generate the final composite indicator. It is composed itself of three sub-indicators: “Forest Non-bird species”, “Forest bird species” and “Forest habitats”. All the three sub-indicators build on distribution data from the reporting of habitat and species conservation status under Article 17 of the Habitats Directive and Article 12 of the Birds directive which describe their distribution at 10km grid resolution. The forest species and the forest habitats proposed to be used for the HNV forest area identification were selected based on expert judgement (ETC/BD) and raster files reporting the count of forest species and habitats were created. At this stage, no weight is applied based on Habitat and Species prioritization, conservation status or endemism. The sub-indicators were then normalized for each European forest type and successively combined not assigning any specific weight to a particular sub-indicator.
The values for this indicator, present in this dataset, ranges between 0 and 1. The values close to 1 mean high presence of habitats and species related to forest, whereas the lower richness are closer to 0. It covers the forested areas of the EU27 Member States except for Cyprus (data from Croatia will be reported starting from the next update regarding the period 2013-2018).


Document Actions
Share with others