Soil Signal 1: Pesticides in soils
Pesticides are often considered important for securing sufficient food and feed quantity and quality. However, this also means that these potentially hazardous compounds are introduced into soil, water, air and crops. Despite the improved effectiveness of and application practices for many currently used pesticides, these substances are nevertheless toxic and often persistent by design — accumulating in soils and risking harm to ecosystems.
Silva et al. (2019) found that more than 80% of soils tested from a number of EU Member States contained pesticide residues: 25% of the samples had one residue and 58% had mixtures of two or more residues. A preliminary analysis based on the EU LUCAS Soil data from 2018 is shown in Figure 1.
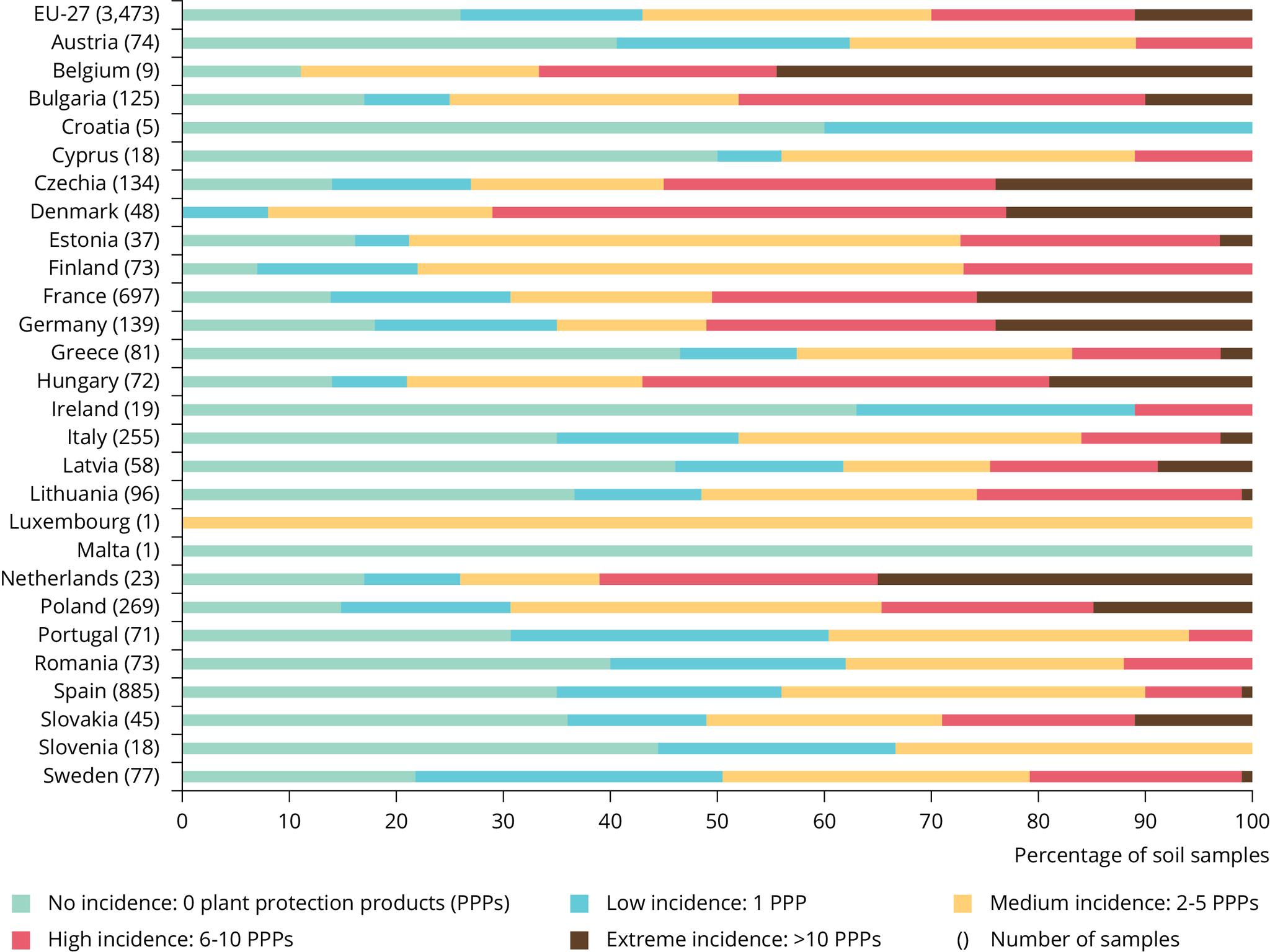
Source: JRC (forthcoming). Data provided to the EEA by the European Commission Joint Research Centre, based on the results of the Lucas soil survey 2018. Due for publication in late 2022 or early 2023.
Click here for different chart formats and data
References
JRC, forthcoming, Plant protection products in European soils, European Commission Joint Research Centre.
Silva, V., et al., 2019, ‘Pesticide residues in European agricultural soils — a hidden reality unfolded’, Science of the Total Environment 653, pp. 1532-1545 (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.441).
Cover image source: © Panagiotis Dalagiorgos, Well with Nature /EEA

Document Actions
Share with others