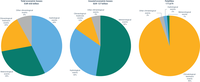
Total economic losses, insured economic losses and fatalities per hazard type.
Hazard types: meteorological hazards, hydrological hazards, climatological hazards (heat waves), climatological hazards (other).

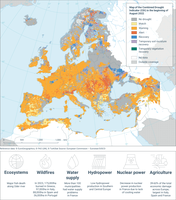
The map shows the drought situation in Europe in the first ten-day period of August 2022 (from 1 to 10 August 2022). The method is based in 6 impact levels. These levels are: "Watch" (yellow colour) when a relevant precipitation shortage is observed, "Warning" (orange) when this precipitation shortage comes with a soil moisture anomaly, "Alert" (red) when these two conditions are accompanied with an anomaly in the vegetation condition, "Temporary soil moisture recovery" (purple) when after a drought episode, soil moisture conditions went below the drought threshold but did not improve enough to consider the episode closed; "Temporary vegetation recovery" (green) when after a drought episode, vegetation conditions went below the drought threshold but did not improve enough to consider the episode closed; "Recovery" (blue) when meteorological, soil moisture, and vegetation normal conditions are recovered.
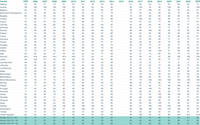
The table shows the countries' reporting performance on the basis of Eionet Core Data Flows since 2005
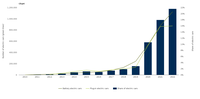
Data Visualization
25 Oct 2023

Data Visualization
25 Oct 2023
In 2020, eleven countries succeeded in decreasing their emission intensities by more than 6%, with Sweden and Finland achieving the highest reductions (19.1% and 7.2% respectively).
This entry points at data related to the "Exposure of vulnerable groups and social infrastructure to climate-related risks" viewer on the European Climate and Health Observatory platform. The viewer analyses the exposure of vulnerable populations (the elderly and unemployed) and social infrastructure (schools and hospitals) to the risk of flooding. It also presents the exposure of social infrastructure to the Urban Heat Island effect for 100 European cities.
This vector dataset provides the climate suitability index values (0-100%) for tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) for 100 European cities for the years 2008-2009 (P90 - 90th percentile).
Aedes Albopictus has become a common occurrence in Southern Europe and transmits diseases such as Zika, dengue and chikungunya. The climatic suitability for tiger mosquito depends on factors such as sufficient amounts of rainfall, high summer temperatures and mild winters. Climate change is anticipated to further facilitate the spread of tiger mosquitoes across Europe by changing temperature and precipitation patterns, thereby increasing the suitable habitat.
Document Actions
Share with others