All official European Union website addresses are in the europa.eu domain.
See all EU institutions and bodiesTo prevent the worst impacts of climate change, European countries have developed national strategies, policies and accompanying measures to mitigate climate change. These include for example targets for greenhouse gas emissions in key sectors of the economy, promoting the use of renewable energy and low carbon fuels or improvements in the energy efficiency of buildings.
Key facts
- In 2023, for the first time, Member States reported on integrated national climate and energy policies and measures, in relation to the various dimensions of the Energy Union, such as: Decarbonisation: GHG emissions and removals; Decarbonisation: Renewable energy; Energy efficiency; Energy security; Internal energy market; Research, innovation and competitiveness. A total of 3 039 policies and measures were reported, by Member States.
- The number of national policies and measures, reported by Member States to reduce GHG, increased by 14 % between 2021 and 2023. A total of 2 332 policies and measures were reported in relation to ‘Decarbonisation: GHG emissions and removals’. Most of the new reported policies and measures are at the planning stage.
- The number of single policies and measures of a Member State is not necessarily related to its ambition level. However, in order to achieve the EU 55% reduction target by 2030, additional climate actions are needed. This requires further strengthening of existing and implementing new policies and measures.
- Most climate change mitigation measures reported in 2023 are economic instruments (e.g., subsidies or feed-in tariffs) or regulations (e.g., energy efficiency standards) primarily targeting energy and transport-related GHG emissions.
- Reporting on quantitative information remains incomplete, especially on the emission savings achieved by implemented measures (ex-post), cost and benefits, and indicators to monitor progress. Completeness of reporting reduced in 2023 in comparison with 2021 reporting year.
- In 2024, a non-mandatory reporting year, three countries (Estonia, Ireland, and Sweden) updated their existing GHG policies and measures information, but no new policies were reported.
The European countries (EU27 + Iceland, Norway, Switzerland) have reported altogether more than 3,000 policies and measures to achieve climate change mitigation and energy targets, such as reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, producing additional renewable energy, or reducing overall energy consumption.
The number of national policies and measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions increased by 14 % between 2021 and 2023
According to the EEA's recent analysis, current policies and measures are expected to deliver a 43 % reduction in GHG emissions by 2030 compared to 1990, while implementing all reported planned (additional) policies could lead the total net reduction to 48 %. Despite this good progress, further effort will be needed by the EU and its Member States to meet the 55 % net GHG reduction target by 2030.
Total number of existing and planned policies and measures reported by the EU27 in 2015, 2017, 2019, 2021 and 2023, and individual countries in 2023
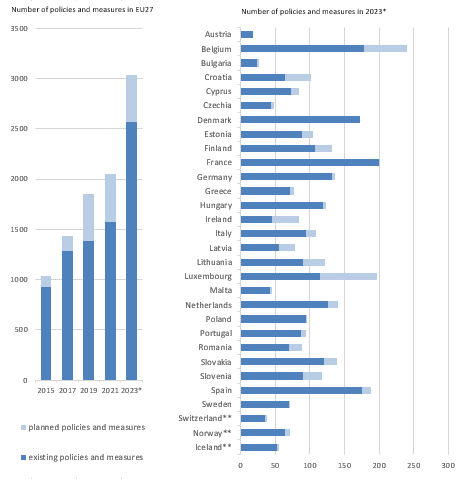
Note: *The increase in the number of reported PaMs in 2023 reflects the increase in scope of reporting, making comparison with previous reporting complicated. Out of 3 039 PaMs reported by the EU27, 2 332 were reported in relation to the dimension ‘decarbonisation: GHG emissions and removals’.
**non-EU countries
Source: Reportnet uploads for obligation "Integrated national policies and measures" provided by the European Topic Centre on Climate Change Mitigation (ETC /CME), 2023.
Consult the latest ETC CM report: Overview of reported integrated national climate and energy policies and measures in Europe in 2023 for a complete analysis on national efforts to reduce GHG emissions, increase renewable energy production, or reduce overall energy consumption.
