All official European Union website addresses are in the europa.eu domain.
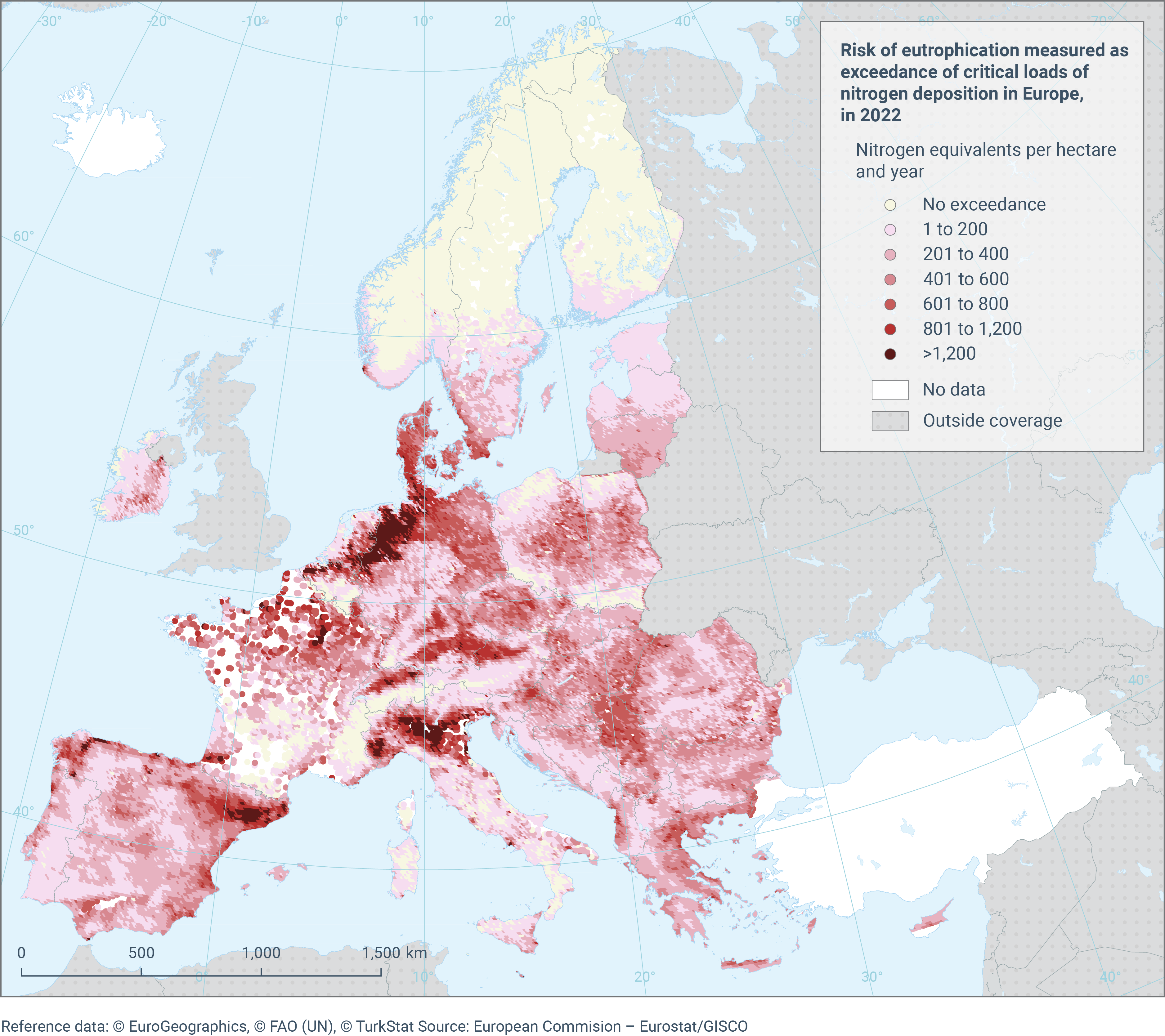
See all EU institutions and bodiesAir pollution threatens biodiversity. Excess amounts of nitrogen can cause eutrophication, disrupting terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems and leading to changes in species diversity, for example in nutrient-poor grasslands. The main sources of atmospheric nitrogen deposition are combustion processes, which result in nitrogen oxides (NOx) being emitted to the air, and ammonia (NH3) emissions from agriculture. Nitrogen deposited in terrestrial ecosystems causes harmful eutrophication when so-called critical loads are exceeded.
Map-package.zip
Loading