3. Survey of reported data for 1997
The location of monitoring stations in EU Member States which are used
for the implementation of the ozone directive and which are reporting over 1997, is
presented in Map 1. Stations located in other European countries which have reported ozone
data on a voluntary basis are shown as well. In total information for 984 stations in 15
Member States has been received; for 100 stations in the six reporting non-EU countries
information has been received. All reporting countries use the reference method (UV
absorption) as prescribed in Annex V of the Ozone Directive, however, at a limited number
of stations chemiluminescence is used.
In 1997 only one exceedance of the threshold value of 360 µg/m3
for hourly values has been reported1: on 18 June, 13.00 a
hourly ozone concentration of 383 µg/m3 was measured at Lykovrissi (Athens,
Greece). This day was the start of an ozone episode in Athens. The station Lykovrissi
reported exceedances of the human health related threshold value of 110 µg/m3
for 8-hourly averaged during the period 18-24 June. During the whole month of June,
concentrations were high in Athens: on 17 days at least one (out of seven) stations
reported an hourly value exceeding 180 µg/m3. On 22 June all seven stations
reported an exceedance with an maximum of 229 µg/m3. See for a more extensive
description of this episode de Leeuw et al. (1997).
A summary of the maximum concentration measured at any of the reporting
stations where exceedance2 of a threshold value is observed is
presented in Table 3. When no exceedances of a threshold have been reported by a country
this is indicated with a dash (-).
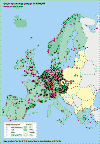
Map 1. Location of ozone monitoring stations as reported by
Member States in the framework of the Ozone Directive for the reference period 1997.
Stations for which other European countries submitted information are shown as well.
Table 3. Maximum ozone concentrations (in
µg/m3) measured during a period of exceedance of threshold values
(reference period 1 January - 31 December 1997). A dash (-) indicates that no exceedances
have been observed; na indicates that no data are available.
| |
180
(1h) |
200
(1h) |
360
(1h) |
110
(8h-a) |
110
(8h-b) |
65
(24h) |
AT |
228 |
228 |
- |
166 |
171 |
153 |
BE |
277 |
277 |
- |
205 |
219 |
171 |
DE |
253 |
253 |
- |
221 |
215 |
214 |
DK |
181 |
- |
- |
141 |
155 |
133 |
ES |
279 |
2791 |
- |
na |
na |
na |
FI |
- |
- |
- |
147 |
136 |
119 |
FR |
1992 |
270 |
- |
184 |
210 |
170 |
GB |
314 |
314 |
- |
188 |
195 |
140 |
GR |
383 |
383 |
383 |
221 |
246 |
138 |
IE |
- |
- |
- |
151 |
131 |
133 |
IT |
353 |
353 |
- |
207 |
230 |
3533 |
LU |
203 |
203 |
- |
166 |
174 |
148 |
NL |
266 |
266 |
- |
183 |
199 |
121 |
PT |
271 |
271 |
- |
204 |
230 |
174 |
SE |
- |
- |
- |
141 |
144 |
128 |
EU-15 |
383 |
383 |
383 |
221 |
246 |
3533 |
CH |
274 |
274 |
- |
182 |
208 |
166 |
CZ |
200 |
200 |
- |
177 |
182 |
148 |
LV |
- |
- |
- |
115 |
127 |
102 |
NO |
- |
- |
- |
162 |
162 |
162 |
PL |
222 |
222 |
- |
163 |
168 |
135 |
SK |
- |
- |
- |
135 |
149 |
122 |
all |
383 |
383 |
383 |
221 |
246 |
3533 |
(a) based on three non-overlapping eight hourly values between
0.00-8.00; 8.00-16.00; 16.00-24.00;
(b) based on the eight hourly value between 12.00 - 20.00;
(1) exceedances of the threshold of 200 µg/m3 have not been
reported; a maximum concentration of 279 µg/m3 is deduced from the information
on exceedances of the threshold of 180 µg/m3;
(2) for a number of stations exceedances of the 200 µg/m3
threshold have not been reported as exceedances of the 180 µg/m3 threshold;
(3) there are clear indications that the maximum concentration refers to an
hourly, not daily averaged value.
As the number of monitoring stations differs widely from country to
country, the absolute number of exceedances is less suitable for comparison. Therefore,
the concept of "occurrence of exceedances" is introduced here. Occurrence of
exceedances is defined as the average number of observed exceedances per country, that is,
the total number of exceedances summed over all the stations of a country divided by the
total number of reporting stations. A summary of occurrence of exceedances is presented in
Table 4. Still, Table 4 has to be interpreted carefully as there are additional reasons
which hamper a comparison between the countries. Firstly, the local environment (in
particular NOx sources) influence the ozone levels; the differences between
countries partly result from the differences in the ratios of street, urban and rural
stations. Secondly, about 20% of the reporting stations show a data coverage of less than
75% (or data coverage is not known); this might result in an underestimation of the number
of exceedances. Also the differences in definition of an exceedance (some countries count
an exceedance when the concentration is GREATER THAN the threshold value, other countries
count it when the concentrations is EQUAL TO OR GREATER THAN the threshold) may introduce
difference in occurrence of exceedances.
Adverse effects of ozone on human health and vegetation will not only
depend on the frequency by which a threshold is violated but also on the severity of the
exceedance. The severity of an exceedance can be expressed by the Accumulated exposure
Over a Threshold (AOT). AOT-values are calculated on basis on hourly concentration
according to:
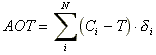
where 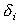 = 0 for
concentration Ci less than threshold T and
= 0 for
concentration Ci less than threshold T and  = 1 when Ci exceeds the
threshold T; N is the number of valid measurements. The AOT is
expressed in concentration x time units, for example in ppm.h or mg.h.m-3.
From the received information it is not possible to calculate an AOT-level as during a
period of exceedance only the maximum concentration is given. As an approximation of the
exposure we can calculate an exceedance rate which is defined as:
= 1 when Ci exceeds the
threshold T; N is the number of valid measurements. The AOT is
expressed in concentration x time units, for example in ppm.h or mg.h.m-3.
From the received information it is not possible to calculate an AOT-level as during a
period of exceedance only the maximum concentration is given. As an approximation of the
exposure we can calculate an exceedance rate which is defined as:
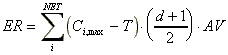
where the summation is now over the total number of exceedance NET
and d is the duration of the exceedance expressed in number of averaging periods, AV.
Similar to AOT, the ER is expressed in concentration x time units, for
example in ppm.h or mg.h.m-3. In Table 4 next to the occurrence
of exceedances, the exceedance rate averaged over the number of exceedances, is given.
Examination of this table shows some - but certainly no perfect - correlation between the
number of exceedances and the severity of exceedance. The data suggests that in southern
countries (Greece, Italy, Portugal) the concentrations are generally much higher during an
exceedance of the information threshold than in the northern countries. The steep fall-off
in the number of exceedances of levels of 180, 200 and 240 µg/m3 in northern
countries compared to the more gradual decrease in southern countries as shown in Figure
2, leads to a similar conclusion.
For each of the countries the lowest and highest 50-, 98- and
99.9-percentile values observed at individual stations are presented in Table 5. In this
table also information on the maximum values is included. Note that the maximum 8-hourly
concentration, as reported in Table 5 is based on a moving average and may therefore
differ from the values in Table 3 which are based on fixed 8-hourly periods. The Czech
Republic has not submitted percentile values for moving eight-hourly concentrations; Spain
has submitted no statistical information at all. Statistics for Latvia and the Netherlands
are not included in the table. In case of Latvia, the data coverage for the submitting
station is below the required 75%; this low data coverage is largely caused by missing
data for the period 1 January - mid April. The information on maximum concentrations and
on exceedances will therefore be reliable. In case of the Netherlands no information on
data coverage has been submitted and therefore the validity of the percentile values can
not be judged. Full details on percentile values and the number of exceedances at the
individual stations is presented in Tables I.3 of Annex I.
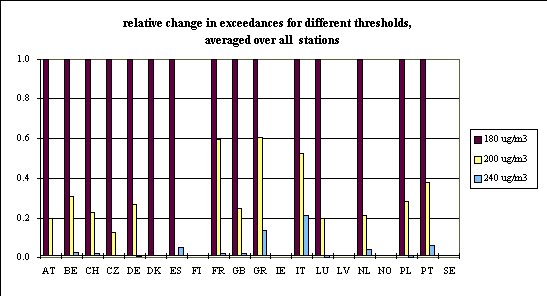
Figure 2. Relative change in exceedances
for the threshold values of 180, 200 and 240 µg/m3. The number of exceedances
of 180 µg/m3 is set to unity; reference period 1 January - 31 December 1997.
For Spain no information on exceedances of 200 µg/m3 has been submitted. For
all countries, the number of exceedances of 240 µg/m3 has been extracted from
the information on exceedances of the threshold of 180 µg/m3.
As ozone concentrations show a high auto-correlation, the correlation
between 1-h and 8-h percentile values is no surprise. Median values for hourly and moving
8-hourly concentrations are very similar. The 98-percentile for 8-h values is generally
about 10% lower than the corresponding 1-h value although this ratio is slightly different
for the various types of stations and has also a meteorological dependence. Detailed
information on the percentile values and maximum concentrations observed at individual
monitoring stations is given in Annex I, Table I.3.3
For a large number of countries additional statistical information on NOx,
NO2 and VOC concentrations has been received. This information is primarily
used here for the classification of stations. Being precursors of ozone, information on
ambient levels of NOx and VOC is essential to evaluate the effectiveness of
ozone abatement strategy. The information voluntary submitted in the framework of the
Ozone Directive is, however, not sufficient for such an evaluation. The limited time
series (four years or less) and generally lack of information on the local environment of
the stations, hampers an analysis of a possible trend in precursor NOx and VOC
emissions. As the reported NO2 and O3 concentrations are not
measured simultaneously, it is not possible to improve the insight in spatial variability
of ozone concentration based on mapping of oxidant (sum of NO2 and ozone)
concentrations. Oxidant concentrations are representative for a larger area as oxidant is
less dependent on local condition and meteorological conditions than either ozone or NO2
(see also Annex II). An overview of the reported NOx, NO2 and VOC
concentrations is given in Table I.4 and I.5 of Annex I.
Table 4. Occurrence of exceedances (OoE; in days) and average
exceedance rate (ER; in (µg.h)/m3 for the threshold value of 180 µg/m3
and in (mg.h)/m3 for the threshold values of 110 and 65 µg/m3);
reference period 1 January - 31 December 1997. na = no data available.
| |
|
threshold
value (in µg/m3) |
| |
number of |
180-1h |
110-8h(a) |
65-24h |
| |
stations (b) |
OoE |
ER |
OoE |
ER |
OoE |
ER |
AT |
111 |
0.1 |
2.7 |
30.5 |
2.9 |
119 |
55.4 |
BE |
25 |
3.2 |
151.7 |
23.1 |
4.7 |
50.4 |
19.4 |
DE |
373 |
1.4 |
52.2 |
25.5 |
3.4 |
64.0 |
24.2 |
DK |
5 |
0.2 |
0.3 |
8.4 |
0.9 |
78.4 |
18.3 |
ES |
36 |
4.2 |
141.9 |
na |
na |
na |
na |
FI |
11 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
6.9 |
0.5 |
128 |
42.7 |
FR |
151 |
1.2 |
13.1 |
21.9 |
2.8 |
64.6 |
24.4 |
GB |
71 |
0.7 |
27.5 |
6.5 |
1.0 |
33.0 |
9.1 |
GR |
13 |
10.1 |
710.1 |
32.0 |
5.2 |
64.6 |
22.7 |
IE |
6 |
0 |
0.0 |
2.7 |
0.3 |
73.3 |
20.7 |
IT |
121 |
12.3 |
863.9 |
33.8 |
5.4 |
68.0 |
51.3 |
LU |
5 |
1.0 |
17.2 |
26.2 |
4.7 |
70.4 |
34.2 |
NL |
39 |
1.2 |
44.1 |
14.5 |
2.4 |
31.5 |
10.2 |
PT |
11 |
3.1 |
160.9 |
22.8 |
4.1 |
52.8 |
23.1 |
SE |
6 |
0 |
0 |
9.5 |
0.9 |
166 |
56.0 |
EU-15 |
984 |
2.6 |
136 |
23.2 |
3.1 |
60.3 |
24.8 |
CH |
13 |
3.7 |
130 |
58.5 |
9.3 |
135 |
67.2 |
CZ |
48 |
0.2 |
3.4 |
28.2 |
2.9 |
112 |
46.9 |
LV |
1 |
0 |
0 |
6.0 |
0.5 |
55.0 |
12.5 |
NO |
14 |
0 |
0 |
6.7 |
1.1 |
147 |
97.3 |
PL |
16 |
0.5 |
11.7 |
15.9 |
1.6 |
79.1 |
29.0 |
SK |
8 |
0 |
0 |
4.8 |
0.3 |
30.3 |
7.6 |
(a) based on the eight hourly value between 12.00-20.00.
(b) note that differences in the number of stations reporting for each of
the threshold levels may occur.
Table 5. Range in reported 50-, 98- and 99.9-percentile
values and maximum observed values (based on hourly and moving eight-hourly average
concentrations, period: 1997) observed at individual monitoring stations in reporting
countries (in µg/m3); na = range in percentile values not available;
? = range in percentile values can not be calculated as data coverage is below 75%, or
information on data coverage is lacking; * = additional information submitted on a
voluntary basis.
| |
1h-P50
|
1h-P98
|
1h-P99.9*
|
1h-MAX
|
| |
min |
max |
min |
max |
min |
max |
min |
max |
AT |
15 |
97 |
90 |
143 |
117 |
176 |
124 |
228 |
BE |
18 |
56 |
96 |
154 |
150 |
203 |
166 |
277 |
DE |
8 |
102 |
63 |
193 |
99 |
225 |
109 |
253 |
DK |
44 |
62 |
90 |
117 |
116 |
153 |
124 |
181 |
ES |
na |
na |
na |
na |
na |
na |
na |
na |
FI |
35 |
74 |
86 |
112 |
106 |
140 |
118 |
179 |
FR |
11 |
97 |
82 |
164 |
111 |
214 |
26 |
270 |
GB |
10 |
64 |
68 |
124 |
102 |
194 |
74 |
314 |
GR |
18 |
56 |
82 |
167 |
117 |
266 |
137 |
383 |
IE |
40 |
66 |
82 |
106 |
na |
na |
114 |
173 |
IT |
11 |
86 |
51 |
186 |
98 |
237 |
121 |
271 |
LU |
20 |
62 |
79 |
146 |
115 |
182 |
131 |
203 |
NL |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
67 |
266 |
PT |
10 |
65 |
44 |
157 |
63 |
177 |
77 |
271 |
SE |
59 |
69 |
96 |
116 |
114 |
147 |
118 |
169 |
CH |
14 |
87 |
116 |
163 |
142 |
205 |
150 |
274 |
CZ |
21 |
80 |
82 |
140 |
106 |
171 |
127 |
200 |
LV |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
|
141 |
NO |
52 |
70 |
88 |
111 |
102 |
146 |
108 |
162 |
PL |
22 |
82 |
90 |
127 |
127 |
185 |
136 |
222 |
SK |
|
50 |
|
113 |
|
130 |
122 |
161 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
8h-P50
|
8h-P98
|
8h-P99.9*
|
8h-MAX
|
| |
min |
max |
min |
max |
min |
max |
min |
max |
| AT |
15 |
97 |
83 |
141 |
108 |
167 |
112 |
174 |
| BE |
20 |
56 |
88 |
175 |
134 |
202 |
143 |
226 |
| DE |
14 |
102 |
55 |
180 |
82 |
219 |
93 |
225 |
| DK |
44 |
62 |
86 |
114 |
109 |
147 |
112 |
158 |
| ES |
na |
na |
na |
na |
na |
na |
na |
na |
| FI |
35 |
75 |
81 |
110 |
92 |
133 |
102 |
147 |
| FR |
14 |
97 |
75 |
159 |
101 |
194 |
15 |
211 |
| GB |
12 |
66 |
62 |
118 |
92 |
178 |
60 |
200 |
| GR |
20 |
57 |
72 |
147 |
97 |
203 |
109 |
252 |
| IE |
39 |
66 |
79 |
104 |
na |
na |
110 |
162 |
| IT |
48 |
48 |
129 |
129 |
162 |
162 |
94 |
230 |
| LU |
22 |
62 |
72 |
140 |
103 |
166 |
110 |
175 |
| NL |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
57 |
199 |
| PT |
11 |
65 |
38 |
154 |
53 |
165 |
57 |
233 |
| SE |
59 |
69 |
96 |
113 |
112 |
142 |
114 |
147 |
| CH |
na |
na |
na |
na |
na |
na |
135 |
209 |
| CZ |
24 |
80 |
74 |
134 |
97 |
160 |
107 |
187 |
| LV |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
|
129 |
| NO |
51 |
70 |
88 |
108 |
101 |
142 |
102 |
147 |
| PL |
23 |
81 |
81 |
124 |
114 |
157 |
125 |
175 |
| SK |
|
50 |
|
105 |
|
120 |
108 |
149 |
1 On 20 June 1997 the Italian station Via
Venezia in Caltanissetta (Sicilia) reported an exceedance of the threshold value of
200 mg/m3 during two hours; as maximum concentration during this exceedance a
value of 379 mg/m3 was reported. This value has not been reported as an
exceedance of the 360 mg/m3 level. According to information from the Italian
data supplier, this value is in error and should be disregarded; another exceedance,
observed at nighttime in the winter at the same station, should be disregarded as well
(Mr. P. Lagrotta, personal communication).
2 In this report exceedances are
counted on a daily basis, that is, a day on which at least one 1h- or 8h-concentration
exceeds the threshold value, is marked as an exceedance.
3 Annex I is only available in computer readable form from the ETC-AQ web-site. In this report a description of
the tables in Annex I is provided.


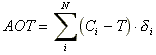

Document Actions
Share with others