All official European Union website addresses are in the europa.eu domain.
See all EU institutions and bodiesAn official website of the European Union | How do you know?
Environmental information systems
Threat status of EU species
Chart (static)
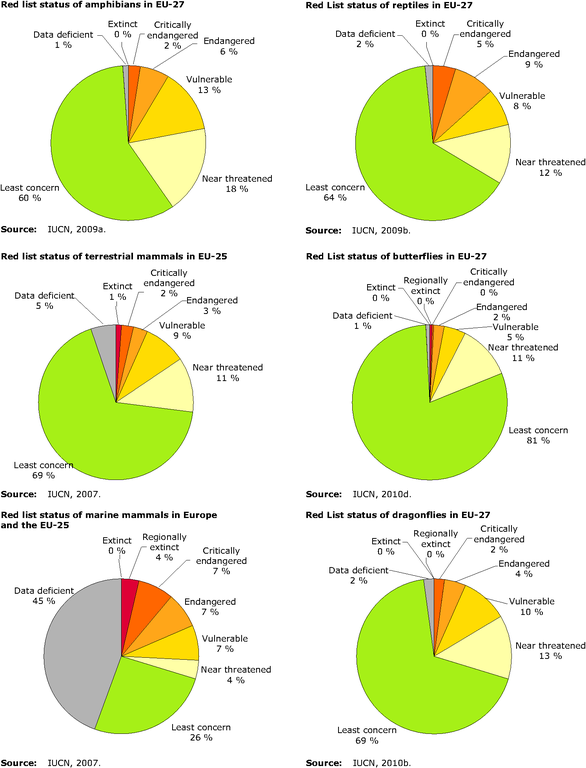
Red list status of amphibians, terrestrial mammals, marine mammals, reptiles, butterflies and dragonflies in EU.
Downloads
Data sources
Metadata
More info
Loading
- European Red List of Butterflies, IUCN 2010
- European Red List of Dragonflies, IUCN 2010
- European Red List of Amphibians, IUCN 2009
- The Status and Distribution of European Mammals, IUCN 2007
- European Red List of Reptiles, IUCN 2009
- Greece
- Poland
- Romania
- Portugal
- Spain
- United Kingdom
- Netherlands
- Belgium
- Germany
- France
- Czechia
- Italy
- Cyprus
- Estonia
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Finland
- Hungary
- Bulgaria
- Malta
- Denmark
- Sweden
- Austria
- Luxembourg
- Ireland
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
2007
2009-2010
Amphibians
- More than 20 % of the amphibians found in the EU are considered threatened and a further 18 % are considered near threatened.
- All amphibian species considered threatened (critically endangered, endangered og vulnurable) at EU level are endemic to the European continent and are found nowhere else in the world.
- Habitat loss, fragmentation and degeneration are the most significant threats to amphibians in Europe.
Mammals
- Nearly one in of terrestrial Europe's mammal species are threatened and a further 11 % are close to qualifying for threatened status.
- Two European mammal species have become globally extinct since AD 1 500 (the aurochs Bos primigenius and the Sardinian pike Prolagus sardus) and a third species is regionally extinct (the grey whale Eschrichtius robustus).
- Habitat loss and degradation is the greatest threat to terrestrial mammals in Europe, whilst the main threat to marine mammals are accidental mortality, pollution and over-exploitation.
Reptiles
- Approximately one fifth of reptiles are considered threatened in Europe and a further 12 % are considered near threatened.
- The majority of threatened and near threatened reptile species, all critically endangered species and the vast majority of endangered and vulnurable species are endemic to both Europe and the EU.
- Habitat loss, fragmentation and degradation are the greatest threats to reptiles in Europe.
Butterflies
- Approximately 7 % of butterflies are considered threatened in Europe and a further 11 % are considered near threatened.
- Two butterfly species have become regionally extinct in recent years (Aricia hyacinthus and Tomares nogelii).
- The main current threat is the loss of their habitats or habitat connectivity due to changes in agricultural practices (intensification or abandonment).
- Dragonflies
- Approximately 16 % of dragonflies are considered threatened in Europe and a futher 13 % are considered near threatened.
- The main current threat is desiccation of their habitats.
