All official European Union website addresses are in the europa.eu domain.
See all EU institutions and bodiesInfluence of climate on household energy consumption per dwelling
Chart (static)
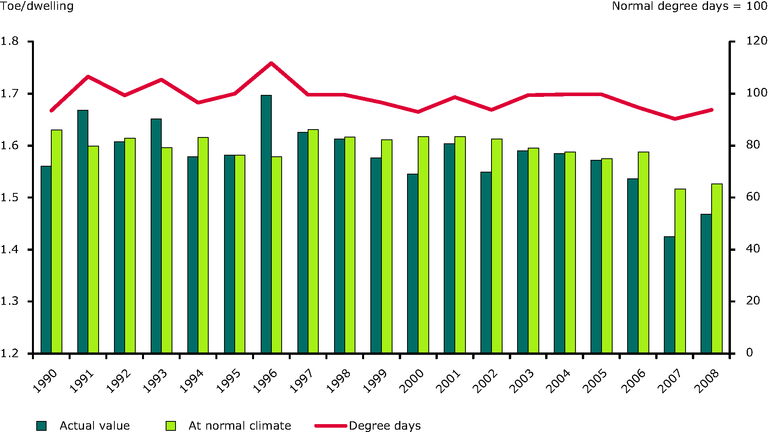
Influence of climate on household energy consumption per dwelling between 1990 and 2008.
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- United Kingdom
Methodology
See indicator ENER022.
Methodology of calculation : energy consumption with climatic corrections (or climate corrected)
Making climatic corrections enable to measure energy savings or energy efficiency trends that are independent on the year-to-year variations in the winter severity.
The most common method of climatic correction is to calculate a fictive consumption at normal climate in a linear way on the basis of the ratio between the normal degree- days (DDn) and the actual number of degree-days (DD)
(case of ODYSSEE or Eurostat). The “normal” winter is based on a long-term average of degree-days value. Eurostat uses a 25 years average (1980-2004)
The experience shows that this simple method over corrects when winters are much milder than the “normal” winter. In some cases (e.g. in ODYSSEE or Denmark), the correction is only applied to a certain proportion of the space heating consumption k (k=90 %) to account for the fact that some losses are not dependent on the number of degree-days.
E = En x K x (DD/DDn) + En x (1-K)
or En = E x 1/ (1-K x (1-DD/DDn))
with E : Energy consumption, En : Energy consumption (climate corrected), DD: heating degree days ; DDn = Heating degree days (25 years average), K= heating share for normal year, or K= r x a with r = heating share for normal year and a = share of heating dependant on degree days (eg 90%)
Additional information
Definition of degree days:
- The actual heating degree days is an indicator of the winter severity, and thus of the heating requirement.
- It is calculated as the sum over each day of the heating period (e.g. October to April) of the difference between a reference indoor temperature (usually 18°C) and the average daily temperature;
- If the average temperature of a day in winter is 5°C, the number of degree day of that day is 13 degree days (18-5).
- The number of degree-days in EU countries is in a range from 700-800 degree-days for Cyprus and Malta to 4000-5000 degree-days in Nordic and Baltic countries (around 2800 degree-days for EU-27 as a whole).
- The daily outside temperature is measured from the various meteorological stations existing in the country and averaged to get a national value.
- The national average is calculated as a population weighted average.
