All official European Union website addresses are in the europa.eu domain.
See all EU institutions and bodiesAdditional information on health impacts from transport noise at EU level in 2017
Chart (static)
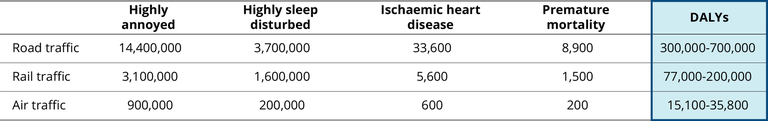
The figure shows information on the number of people estimated to be highly annoyed and highly sleep disturbed due to noise from road, railway and aircraft. It also shows information on the estimated number of cases per year of IHD and premature deaths. All the values of the table are used to calculate the Burden of Disease (BoD) in Disability Adjusted Life Years (DALYs)
- Austria
- Belgium
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Ireland
- Italy
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Malta
- Netherlands
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
Methodology
The indicator is based on the following data:
- Data reported by EU Member States in accordance with Directive 2002/49/EC (the END) . In addition, a disaggregated assessment which includes EEA member countries (excluding Turkey) is presented. The data used cover the population exposed to noise above END thresholds (i.e. noise levels of 55dB or higher during the day-evening-night period and to night-time noise levels of 50dB or higher) for the following noise sources: roads with more than 3 million vehicle passages per year, railways with more than 30,000 train passages per year and airports with more than 50,000 aircraft movements per year, as well as all roads, railways, airports and industries in urban areas with more than 100,000 inhabitants.
- Exposure-response functions for high annoyance and high sleep disturbance presented in the Environmental noise guidelines for the European region (WHO Europe, 2018). These are generalised functions and are in line with Annex III of the Environmental Noise Directive (EC, 2020).
- Data on age distribution from Eurostat (ETC/ACM, 2018). The number of highly annoyed and highly sleep disturbed people is calculated from only the population over the age of 17 years because the exposure-response functions are based on responses from the adult population and cannot be extrapolated to children.
- The calculation of IHD incidence, premature deaths and DALYs are described in ETC/ACM (2018) and EEA (2020).
Additional information
• The risk of developing negative health effects when exposure is long- term, start to occur below the END thresholds. The WHO recommends reducing noise levels to 53 dB Lden and 45 dB Lnight for road traffic, 54 dB Lden and 44 dB Lnight for rail traffic, and 45 dB Lden and 40 dB Lnight for air traffic.
• This chart is based on data officially reported by countries under the EU Environmental Noise Directive (2002/49/EC). There are inconsistencies across countries, as Member States were allowed to use their own national methods.
• There may be double counting in locations where there is exposure from multiple sources. It is estimated that double counting is less than 13% for high annoyance and 16% for high sleep disturbance (ETC/ACM, 2018).
• High annoyance and sleep disturbance are prevalent cases, and ischaemic heart disease and premature mortality refer to are incident cases per year. Values are rounded.
